Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies
Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Translational Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies, Principle of Moments, Rotational Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies, Toppling of Rigid Bodies, Toppling with Application of Force & Toppling with Linear Velocity etc.
Important Questions on Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies
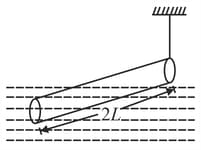
A slender homogeneous rod of length 2L floats partly immersed in water, being supported by a string fastened to one of its ends, as shown. The specific gravity of the rod is 0.75. The length of rod that extends out of water is
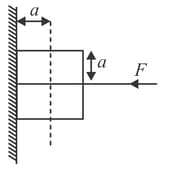
A force is applied on the square block of edge length such that the block remains stationary on the vertical wall. Then false statement is
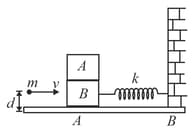
Two identical cubes and of same mass and side are placed one over the other as shown in figure. is attached to one end of a spring of force constant . The other end of the spring is attached to a wall. The system is resting on a smooth horizontal surface with the spring in the relaxed state. A small object of mass moving horizontally with speed at a height above the horizontal surface hits elastically the block along the line of their centre of mass. There is no friction between and :
(a) find the minimum value of (say ) such that block will topple over block
(b) if find the amplitude of oscillation of block spring system.
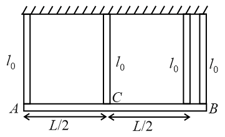
A uniform rod of mass and length is suspended from four identical wires with two wires at end , one at end and one at centre. Natural length of wires is . Tensions in wires connected at is given by . Find . (Diagram is not drawn to scale)
A rigid body is observed in equilibrium in a particular non-rotating non-inertial frame. What can you conclude, if the body is observed from an inertial frame?
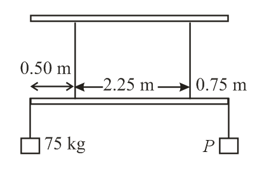
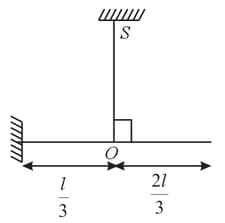
A light beam suspended with the help of two ropes supports two loads as shown in the figure on the next page. The load at the left end is of and the load at the right end is unknown. The maximum tension that either of the rope can bear is . In an experiment, mass of the load is gradually increased from zero. If the rod remains horizontal in equilibrium, which of the following conditions must be satisfied?
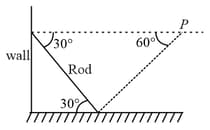
A uniform rod rests against a smooth vertical wall and a rough horizontal surface A horizontal force is applied at the center of mass of the rod such that the rod is in static equilibrium and the resultant of and the weight of the rod intersect at the point shown in the figure. The angle of friction between the rod and the horizontal surface is :
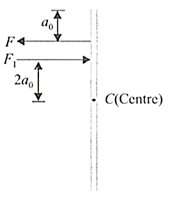
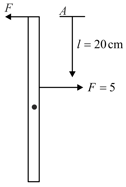
A thin rod of mass moves translationally with acceleration due to two antiparallel forces as shown. If then
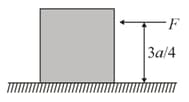
Consider a uniform cubical box of side on a rough floor that is to be moved by applying minimum possible force at a point above its centre of mass (see figure). If the coefficient of friction is the maximum possible value of for box not to topple before moving is ________
_____ is in the middle of the lever of second class.
The mechanical advantage of a lever of third order is always less than _____.
The knife is a lever of the first type.
A body is acted upon by two unequal forces in opposite directions, but not in the same line. The effect is that
A rod of mass and length is suspended from a vertical wall and kept horizontal by a massless vertical thread as shown. The tension in the thread is,
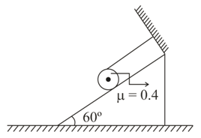
A solid cylinder of mass is wrapped with a string and placed on a rough inclined plane as shown in the fig. Then the frictional force acting between cylinder and plane is
A uniform cube of side a & mass m rests on a rough horizontal table. A horizontal force is applied normal to one of the faces at a point that is directly above the centre of the face, at a height above the base. The minimum value of for which the cube begins to tip about an edge is -----.(assume that cube does not slide).
A spool is pulled at an angle with the horizontal on a rough horizontal surface as shown in the figure. If the spool remains at rest, the angle is equal to
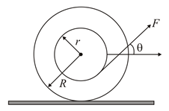
A rod of mass and length is hinged about one end and a particle of mass is attached to its other end. If it is kept horizontal with the help of a spring of spring constant as shown in the figure. Find the extension in spring:-
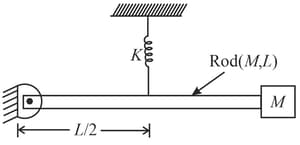
An engineer is designing a conveyor system for loading lay bales into a wagon. Each bale is 0.25 m wide, 0.50 m high, and 0.80 m long (the dimension perpendicular to the plane of the figure), with mass 30.0 kg. The center of gravity of each bale is at its geometrical center. The coefficient of static friction between a bale and the conveyor belt is 0.60, and the belt moves with constant speed. The angle of the conveyor is slowly increased. At some critical angle a bale will tip (if it doesn't slip first), and at some different critical angle it will slip (if it doesn't tip first).
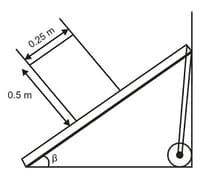
Find the first critical angle (In the same conditions) at which it tips..
A thin uniform rod of mass m and length is moving translationally with acceleration due to two antiparallel forces, as shown. One of the forces is . Find the maximum value of acceleration for which rod may move translationally.